What is Big Data Analytics? The Ultimate Guide for Beginners

If you’re not a data scientist, the term “big data analytics” might sound a bit intimidating. But it doesn’t have to be! In this guide, we’ll give you an overview of what big data analytics is and why it’s important. We’ll also cover some of the ways that businesses use this type of technology to solve problems more effectively.
What is Big Data Analytics?
Big data analytics is a process that uses sophisticated algorithms to turn large datasets into actionable insights. It’s used to solve complex problems and make better decisions, which is why it’s also known as predictive analysis.
Big data analytics has been around since the early 1990s, but its use has increased significantly since then due to the rise of big data technologies—like Hadoop—that make it easier for businesses to do more with their data. It can be applied in many industries, including healthcare, manufacturing, and retail.

History of Big Data Analytics
The term “big data” was first used in 1988, and it refers to the massive amount of data that companies produce. It has gained popularity over the years as technology has evolved, and the amount of information available has increased. Companies are now able to collect more data than ever before and analyze it for insights into their customers.
Big Data Analytics is a relatively new field that has emerged as a result of the rapid growth of data collection and storage. It started with the rise of the internet, which has led to an explosion in the amount of data available to analyze. With this boom came the demand for new ways to store, analyze and interpret large amounts of information.
The term “Big Data” was first used by Blake Commagere at Microsoft in 2002 when he spoke about how companies were using large amounts of unstructured data from multiple sources for business purposes. He stated that this type of information could be analyzed using statistical modelling techniques such as regression analysis or clustering algorithms.
Statistics on Big Data Analytics
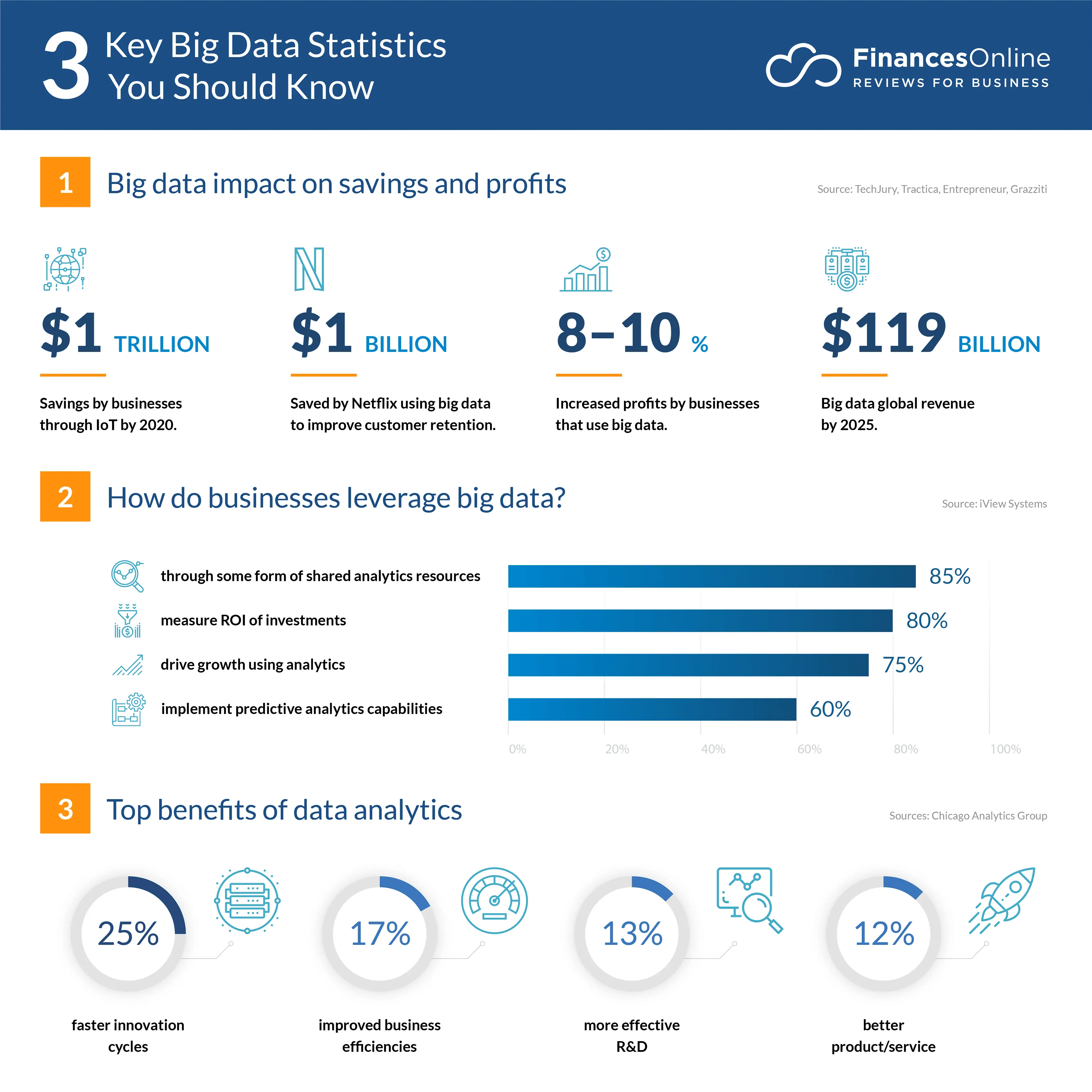
- Half of all companies use big data analytics to track sales, marketing, and customer service efforts.
- By 2022, more than 70% of all data will be unstructured, which means it will be harder for companies to use traditional methods for analyzing it
- 46% of companies use big data analytics to track customer behaviour online.
- Big data analytics jobs are expected to grow by 14% over the next 10 years.
- 64% of companies use big data analytics to improve products or services by looking at previous customer feedback and reviews.
- In fact, by 2022, the global Big Data analytics market will be worth more than USD 117 billion.
- In 2022, there will be an estimated 12 million jobs available for people who are skilled in big data analytics. This number is expected to grow to 14 million by 2025.
Types of Big Data Analytics
Big Data Analytics is a hot topic these days. Many companies are looking for ways to make use of the massive amount of data they have on hand, but they’re not sure where to begin. There are 3 basic types of big data analytics: descriptive, predictive, and prescriptive.
1. Descriptive Analytics
It involves analyzing past data to better understand trends in your business or industry. For example, if you’re a retailer with sales locations across multiple states and want to know where demand will be highest next holiday season so you can stock up on inventory accordingly, descriptive analytics can help you do just that!
2. Predictive Analytics
It uses historical data to predict future trends based on certain variables—for example, if our retailer wants to know whether they should open more locations in Texas next year, predictive analytics could tell them exactly where they should place those new stores.
3. Prescriptive Analytics
It goes one step further by using historical data to determine what changes should happen next—for example, if our retailer wants to know which of their existing locations should be expanded.
Read More: What is Data Analytics? A Complete Guide
Big Data Analytics Tools & Technology
1. Apache Hadoop
Apache Hadoop is a framework for the storage and processing of large volumes of data. It’s a distributed storage system that divides up the data into pieces, which are then stored on multiple machines in one or more locations (multi-data centre), and has applications process it on the fly as it comes back together again.
The technologies within Hadoop include HDFS, MapReduce, Apache Hive, Apache Pig, and Apache Sqoop to name just a few.
Apache Hadoop’s role in big data analytics is primarily to provide an infrastructure for capturing and storing large amounts of unstructured data at scale.
However, once captured and stored this way it can also be used directly by analysts as well as processed via other BI tools such as Tableau or Qlik View along with many others that are listed later on this page.
2. Spark
Spark is a fast and general engine for large-scale data processing. It provides high-level APIs in Java, Scala, and Python, and an optimized engine that supports general execution graphs. Spark can process data up to 100x faster than Hadoop MapReduce in memory, or 10x faster on disk.
Spark is designed to be resilient against failure as well as scalable to run on thousands of nodes. It can run standalone or distributed across clusters of any size and architecture.
3. Apache Flink
Apache Flink is an open-source stream data processing framework. It is a distributed streaming data processing engine for batch and real-time data.
Flink’s runtime is implemented in Java, but its APIs are language agnostic. The core API consists of two high-level interfaces: DataStream and Table. A DataStream represents an unbounded sequence of elements that can be either primitive types or objects.
A Table represents a finite number of elements with typed columns (referred to as fields), where each element has a key associated with it.
4. Python and R Scripts
Python and R are two of the most popular programming languages. It is a general-purpose programming language that is used for data science, machine learning, and more. R is a statistical programming language that can be used to analyze data sets and produce visualizations.
Python can be used to create complex models through its framework PyTorch or TensorFlow, while R has some frameworks such as ggplot2 which makes plotting much easier than in Python.
You might choose one over the other depending on your use case; however, both are good enough tools for any kind of analytics project!
5. Microsoft Azure (HDInsight)
Microsoft Azure (HDInsight) is a cloud-based big data analytics service. HDInsight is a Hadoop-based service, which means it can process large amounts of data stored in the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS).
6. Tableau BI Platform
Tableau BI Platform is a business intelligence (BI) tool that helps users visualize data. It has been used by many companies to create dashboards and reports.
This tool is easy to use and has a user-friendly interface, which makes it a very popular choice among people who are interested in data analytics for business purposes.
Why is Big Data Analytics Important?
Big Data Analytics allows companies to analyze large amounts of data quickly and efficiently so they can make better decisions about how they operate their business. But why is this important? Why should you care if a company uses Big Data Analytics? Here are just a few reasons:
1. Improved analysis
It helps companies find new ways to improve their products or services by analyzing how customers use them.
2. AI-enabled prediction
It helps companies predict trends to be prepared for changes in the market before they happen.
3. Identify problems
It helps companies identify problems before they occur so that quick action can be taken when necessary.
4. Help become more efficient
Big data analytics allows companies to become more efficient by automating processes that would normally take up tons of time.
5. Analyze customers better
It helps you understand your customers better. You can find out what they like and don’t like, and tailor your products or services accordingly.
How Does Big Data Analytics Works?
If you’re wondering how big data analytics works, you’re not alone. Many people are confused by the term and aren’t sure how it applies to them, but the truth is that big data analytics is a powerful tool that can be used in a variety of different ways. There are three main steps involved in big data analytics.
1. Collection
This involves collecting all of your company’s data in one place so you can analyze it later. This can include information about customers, transactions, sales numbers, inventory levels, etc.
2. Analysis
Once information is collected, it’s time to analyze it! This means looking for specific trends in customer behavior or examining how certain products perform against each other in different markets. The aim is to identify relationships between different variables so you can come up with better ways to improve your business operations or products or services.
3. Interpretation
Once you’ve identified those relationships between variables, it’s time for interpretation—figuring out what those correlations mean for your business going forward.
Top 5 Uses of Big Data Analytics
Data analytics has become a critical part of the modern business landscape, and it’s not hard to see why. With so much data available, it’s important to know how to use it effectively. Here are some of the top uses of big data analytics:
1. Advertising
Big data can help advertisers target potential customers more accurately than ever before, allowing them to reach out through the channels that will resonate with those customers most strongly.
2. Customer Service
Big data allows companies to be more responsive when it comes to helping customers because they can see what their customers need and want immediately and take action on that information in real time.
3. Marketing
Big data allows marketers to better understand their customers’ behavior by collecting and analyzing information from multiple sources—including social media posts, web browsing history, and even emails sent by consumers.
This helps create more personalized marketing campaigns that resonate with specific audiences rather than trying to reach everyone at once with one message about your product or service offerings.
4. Financial Analytics
Financial analytics helps businesses make better financial decisions by using data to analyze financial trends over time or across different industries or geographies.
This kind of data analysis can help identify opportunities for growth as well as risks that could negatively affect profitability if not addressed properly early on before they become too large for smaller companies to overcome without heavy losses incurred by those involved along with additional expenses.
5. Fraud Detection
Fraud detection uses big data analytics to identify irregular behaviour patterns that indicate potential fraud before it happens.
Future of Big Data Analytics
The future of Big Data Analytics is bright. Big Data has been used for decades now, but it’s only recently that we’ve begun to understand its true potential. It is used to predict trends as well as create new ones. Big Data can help businesses make more accurate decisions about their products, services, and marketing strategies. We’ve seen some incredible things happen with the use of Big Data in recent years.
Amazon was able to predict which books would sell well before they were published. This allowed them to invest more money into their authors’ careers and gain an edge over their competitors.
Netflix uses data analysis to determine which movies are going to be popular based on what people have already watched—and then they invest heavily in those projects so they’ll get a return on their investment when they’re released!
Facebook uses machine learning algorithms to determine what kind of content each user wants to be based on what they like or comment on most often; this means they can tailor ads specifically towards those users’ interests and preferences, which helps them maximize ad revenue while also providing customers with relevant content that’s useful.

Conclusion
Big data analytics tools are used to analyze and process a large amount of data. These tools are designed to solve problems that a standard database cannot. The best part about this technology is that it’s growing every day, so stay tuned for more updates!
FAQs on Big Data Analytics
Big data is an umbrella term for any dataset that is too large for traditional database systems to store and analyze using standard techniques. Data sets can be structured or unstructured, human-generated or machine-generated, and collected from the real world or online sources.
When you have a dataset that requires special handling, like massive amounts of video data or sensor readings from a smart city project, it’s probably big data.
Big data analytics is the process of collecting, analyzing, and interpreting large amounts of data. The data can come from a variety of sources, including social media platforms like Facebook and Twitter, mobile devices, websites, or even physical sensors. The analysis can take place onsite or in the cloud.
Big data analytics allows companies to make better decisions based on past and current performance. For example, if you’re looking at your sales numbers over time, you might be able to identify seasonal trends that you didn’t know about before—and then use those insights to plan for the future. It can also help you discover new opportunities for growth within your industry or market share by identifying trends that competitors aren’t seeing yet.
The first step is gathering all relevant data from various sources (such as an internal database or third-party cloud service). Then you need to organize it into useful categories so that you can identify patterns that are meaningful for your business. Finally comes analysis itself: finding meaning in those patterns and applying them toward some goal or outcome that will benefit your company overall.
The benefits of big data analytics include:
-Understanding your customer base better so you can offer better products and services for them
-Helping you make better business decisions that will lead to more sales and profit for your company
-Helping you improve customer service by understanding what your customers want and need to create a better experience for them.
Traditional analytics usually involves analyzing smaller amounts of data in an isolated environment. Big data analytics often requires a mix of technologies and processes to handle large volumes of unstructured data that are typically stored in cloud storage systems or other non-relational databases.
Big data analytics helps companies make better decisions by providing insights into their operations, customers, and competitors.
The technology helps businesses identify areas for improvement and opportunities for growth based on historical sales patterns or social media activity.
It helps predict future trends based on current events such as weather patterns or geopolitical developments (such as elections).
Complex algorithms are those that require large amounts of computing power to run efficiently. These algorithms can be applied to large datasets (known as “big data”) that would be impossible to analyze with traditional methods. This includes machine learning and artificial intelligence.
The first thing you should do is get yourself some data. It’s pretty easy—just go online, download some files from the internet, or find someone willing to give you access to their data. Once you have that data, you can start analyzing it and seeing what kind of insights come out of it.
Big data can look like anything! It could be a spreadsheet with hundreds of columns and rows, a picture that someone uploaded on Instagram yesterday—it doesn’t matter as long as there’s enough information in there for us to work with. The more information there is, the better!
It requires significant investment in both time and money, but there are many benefits associated with using this technology: increased productivity; better customer service; increased revenue through better product offerings; improved quality control measures; improved efficiency levels; reduced costs related to employee training (among others).





